
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Legitimate allows agencies and developers to create entirely custom digital experiences on the Legitimate platform for a given set of tags.
Legitimate's API can be used to redirect to custom web applications or even native app experiences via two different approaches. This page covers the simple flow when redirecting to another web-based application. For information on native app integration, please refer to Native App Implementation
The Legitimate Tags are pre-programmed to link to the Tap by Legitimate web app that then be configured to redirect to your own website.
Legitimate's NFC Tags can be configured to redirect to a different domain or URL with the verification parameters from the tag to create an entirely new user flow and digital experience. This is extremely useful to redirect users to a custom web experience, or redirect to a native mobile app experience.
By default, Legitimate's NFC Tags are pre-programmed to open Legitimate's web URL first and then redirect to another desired URL. Legitimate will collect analytics data before redirecting.
The URL parameters can then be used to call the tag related APIs.
Each time an NFC tag is scanned, a new set of verification parameters will be generated. Therefore, if you are intending to use the Tag URL Redirect features, it is extremely important to note that . This is meant to protect the connected products from counterfeit and ensure that each scan is unique.
To configure the redirect URL, please login to the , open the configuration page for the desired SKU, and set the Redirect URL field.
User taps the tag with their phone and opens the link popup
The browser opens
The uid, ctr, and cmac is used to verify the tag's authenticity and get information about the content for the tag.
The browser is then redirected to your own page with the same parameters https://www.yourdomain.com/page/name?uid=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX&ctr=YYYYYY&cmac=ZZZZZZZZZZZZ
Your own page must now call our APIs to verify the digital signature payload that is present in the query parameters.
Please reference our Getting Started guide to see how to implement this verification via a simple JS snippet
Alternatively, you can implement this verification yourself using our API Resources to create a more robust user-experience.

https://verify.legitimate.tech/?uid=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX&ctr=YYYYYY&cmac=ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZhttps://www.yourdomain.com/experience/?uid=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX&ctr=YYYYYY&cmac=ZZZZZZZZZZZZZLegitimate allows agencies and developers to create entirely custom digital experiences on the Legitimate platform for a given set of tags using our APIs.
Direct access to our APIs are available to our enterprise clients. Different plans are available depending on the number of tags supported, API usage limits, custom domains for endpoints, and CORS domain allowlists.
API request and response interfaces are subject to change. Changes will be versioned. All customers will be notified of changes and provided upgrade instructions.
All standard tag resources can be accessed from our external API gateway domain. This domain can be accessed without authentication tokens, API keys, or CORS restrictions.
A fair usage rate limit per API endpoint and per IP or browser client applies. Contact us to request an API key if you expect high usage rates.
Our API endpoints allow you to build a more robust user experience. For example, you can call a to obtain the digital ID and blockchain information associated with the tag. With the given information about the digital ID, you can then call our APIs to the digital ID to a given user wallet or ownership when the item is sold or given away.
Below, we've suggested several considerations to take into account when building your application.
The initial state of the digital ID token is when the tag has been tapped for the first time. The ownership of the token is ready to be claimed by the user.
We suggest a preview of the product metadata and digital experience, as well as a short summary of what to expect before asking the user to login or connect their wallet to claim the NFT.
owner_address = null
After the user has claimed ownership of the digital ID and the token has been transferred to their wallet, anyone who has access to the phygital item can be shown exclusive digital content. Keep in mind that owners often let their friends and family tap the tag as well so any content or digital activations that can encourage sharing can help expand your reach and encourage more engagement.
owner_address = 0xaBcD...
In the event that a link generated by the NFC tag is shared and reused, or invalid tag information is passed in, an error page should inform the user to tap the tag on the item again.
(optional)
For collectible items and items that may be resold, traded, and ownership transferred, we suggest adding the ability for owners to reset the ownership so the token can be claimed again. Because Legitimate pays blockchain transaction fees, resetting ownership and allowing new owners to start over with the claim process is a more seamless experience. The old owner can reset the token before giving the item away, or if the old owner forgot to reset, the new owner can also reset and claim the token as if were new.
Use our provided javascript function in your own HTML website to easily verify the digital signatures emitted by Legitimate's NFC tags
For convenience, Legitimate provides a simple javascript implementation of the API verification mechanism required to validate the digital signatures emitted by NFC tags. You can see a full HTML example here.
To get started, simply add our minified javascript function to the top of your HTML <head> block. Make sure this is at the top of the <head> block as it is required to load first.
This script contains sensible defaults that will hide the entirety of your page's contents until after the digital signature verification is complete. You can see the un-minified implementation of this script .
This script calls the exact same API endpoint as described in by passing through the verification parameters present in the URL query parameters. If the verification is successful, the contents of your HTML <body> will be displayed as normal.
By default, the snippet will display an error message if the digital signature verification fails. You may add custom error messages by adding the following HTML elements to your page.
The inner contents of an HTML element with the following id legitimate-expired-cmac-message will be used as the error state content if the verification fails due to the verification parameters being reused.
Our API is designed in such a way that each tag verification can only occur once with a given set of parameters. This is to prevent customers from sharing or replicating any URLs or links emitted by the NFC tag.
The inner contents of an HTML element with the following id legitimate-custom-error-message will be used as the default error state content if the verification fails.
Smart contracts can be deployed by Legitimate or by third parties. The primary reason to deploy your own smart contracts is if you want to make sure that the contract owner and deployer name on third party platforms properly reflect your own entity (i.e. Opensea).
In the case of third party deployments, Legitimate's blockchain address (legitimatetech.eth on my EVM compatible blockchains) will need to be assigned the in order to perform unlock and claim functionality for our hosted services.
If token recovery and ownership reset is desired for processing returns or managing resales, the should be assigned as well.
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
(function(){var a=document.createElement('style');a.innerHTML=`
body { display: none !important; }
`;document.head.appendChild(a);var b='https://api.legitimate.tech/external/v1/tags/verify';document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded',()=>{console.log('DOM loaded, making API request');fetch(b,{method:'POST',headers:{'Content-Type':'application/json'},body:JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(new URLSearchParams(window.location.search)))}).then(async A=>{var _=await A.json();if(!A.ok){A.status===422&&_.errors.cmac.indexOf('has expired')!==-1?c('expired_cmac'):c();return}!_.errors?a.innerHTML=`
body { display: block !important; }
#legitimate-custom-error-message { display: none !important; }
#legitimate-expired-cmac-message { display: none !important; }
`:c()}).catch(()=>c())});function c(B='default'){let C=document.getElementById('legitimate-error-message-container');!C&&(console.log('Creating error message container'),C=document.createElement('div'),C.id='legitimate-error-message-container',document.body.appendChild(C));let _c=`
<div style="font-family: sans-serif; color: red; padding: 2rem; text-align: center;">
An error occurred. Please try again later.
</div>
`;if(B==='expired_cmac'){var d=document.getElementById('legitimate-expired-cmac-message');d&&(console.log('Using expired cmac error message'),_c=d.innerHTML)}else{var e=document.getElementById('legitimate-custom-error-message');e&&(console.log('Using custom error message'),_c=e.innerHTML)}C.innerHTML=_c;a.innerHTML=`
body { display: block !important; }
body > *:not(#legitimate-error-message-container) { display: none !important; }
`}})();
</script>
<!-- other code that may need to go into the head element -->
</head>https://api.legitimate.tech/external/<div id="legitimate-expired-cmac-message" class="hidden">
<!-- Expired CMAC Error Message -->
</div><div id="legitimate-custom-error-message" class="hidden">
<!-- Your content here -->
</div>Legitimate's smart contracts are designed to allow multiple parties including Legitimate, third party developers or agencies, and the brands or creators themselves to work together and share permissions to interact with the contract on-chain.
Our main token smart contract is open source and available here on GitHub: https://github.com/LegitimateTech/lgt-phygital-nft-v3
Our contracts are broken down into three categories:
The Base contracts cover the underlying functionality of the Locking Mechanism. They are intended to be abstract classes that can be augmented with an ERC721 implementation.
These contracts can be found .
The Locked721 and Locked721Psi contracts extend the base contracts and provide their own respective implementations of ERC721. Locked721 uses OpenZeppelin's ERC721 implementation, whereas Locked721Psi uses the ERC721Psi implementation.
These contracts can be found .
Legitimate further extends the Locked721(Psi) contracts with additional business logic and functionality to serve our partners and clients. These contracts add additional access control roles, logic, and functionality. This includes service terms, recovery capabilities, as well as custom metadata handlers that augment the Locking Mechanism.
These contracts can be found .
We believe that both the physical and the digital parts of any given connected product should belong to the same owner.
In order to ensure that ownership of both the digital ID and the physical product remain in sync, we introduced a locking mechanism that locks the digital ID metadata upon transfer and unlocks when owners submit a valid request containing a checksum emitted by NFC tags programmed according to the Legitimate protocol.
This locking mechanism is an implementation of , a decentralized digital ID proposal meant to bind digital IDs to a single given owner. However, we introduce the ability to set digital ID locks on a more granular level, with the ability for this state to be mutable.
Lock state mapping for tokens
Legitimate Tags contain the NXP NTAG 424 DNA chip. It utilizes NFC technology and is secured by an industry standard encryption algorithm called AES-CMAC. NFC stands for near field communication, a technology that enables devices to read data from NFC tags, tiny microchips with antennae embedded inside stickers, tags, or other materials. Similar technology powers hotel room keys, contactless credit cards, transit passes, and access key fobs. These tags do not contain batteries.
We chose NFC technology because most modern smartphones released in the last few years already have NFC readers built in. They are located at the top of the Apple iPhone and middle of most Android phones.
Our Legitimate Tags feature a secure industry standard encryption called AES-CMAC which prevents our tags from being copied or duplicated. The tags contain a secure enclave that stores a 128-bit private key which cannot be read and requires the same private key to reprogram the tag. A counter on the tag stores the number of times the tag has been tapped and read. The AES-CMAC algorithm then computes a checksum based on the number of reads, the tag's unique identifier, and the private key programmed into the tag. Our servers will then validate the checksum and make sure it matches the read count and tag identifier. Checksums submitted to our servers are tracked and cannot be used again.
Legitimate's encoding process programs the Legitimate Tags to use the AES-CMAC algorithm to compute the URLs in the following format in order to submit to our servers for verification.
Copy
uid - unique identification code of the Legitimate Tag (14 hex characters)
ctr - counter for the number of reads of the Legitimate Tag (6 hex characters)
cmac - AES-CMAC checksum signature (16 hex characters)
The tags can be tapped and read more than 200,000 times and will retain data for more than 30 years. They can be operated in -30℃ to 70℃ temperature and a protective casing can be added for additional heat and water resistance as well.
Please see our Tag Types for more details.
// stores the locked state for each NFT
mapping(uint256 tokenId => bool locked) tokenLock;If you already have a native app, you can also leverage native NFC reading capabilities within the app to read NFC tags programmed by Legitimate. To do so, please refer to the standard documentation to trigger the NFC reading capabilities of the mobile app operating system that you are developing for.
For further clarity, your application must be able to read NFC tags programmed to emit data in NDEF format. This is a fairly standard capability, with support from all major mobile operating systems and frameworks. We've included links to some standard libraries and resources below:
(multiple libraries exist)
After successfully setting up NFC read support in your native application, you should be able to trigger an NFC reading session on your phone. Scanning a Legitimate NFC tag should yield data in the following format:
The URL parameters can then be used to call the tag related APIs.
Each time an NFC tag is scanned, a new set of verification parameters will be generated. Therefore, if you are intending to use the Tag URL Redirect features, it is extremely important to note that . This is meant to protect the connected products from counterfeit and ensure that each scan is unique.
User opens Native App and triggers an NFC read action
iOS applications will trigger a native OS-level user NFC prompt
The NFC tag is read and NDEF data is returned to the mobile app
The uid
Direct access to our APIs are available to our enterprise clients. Different plans are available depending on the number of tags supported, API usage limits, custom domains for endpoints, and CORS domain allowlists.
You can call a to obtain the digital ID and blockchain information associated with the tag. With the given information about the digital ID, you can then call our APIs to the digital ID to a given user wallet or ownership when the item is sold or given away.
See our page for more documentation about the APIs.
POST /v1/tags/verify
Verifies the tag's authenticity via the unique uid, ctr, and cmac generated by each tap of the Legitimate Tag. This API will only return the success response the first time it is called with the correct tag information. Subsequent calls will return the HTTP status 422 and the error message has expired.
Headers
Body
Response
POST /v1/tags/claim
Transfers the digital ID (also known as digital token, or NFT) associated with the tag to the specified user address. The uid, cmac, and ctr must be from the latest successful verify attempt. All previous verifications are invalid to prevent users with old links from claiming.
Headers
Body
Response
Product metadata is derived from a URL that contains a base_uri as well as a file name that corresponds with the tokenId or locked state.
This metadata can then be generated , or via a separate service such as IPFS or AWS.
When a token is locked, it can be configured to display a separate set of metadata for the NFT including image, animation, title, and description.
For projects and clients that want the ability to customize on-chain interactivity and have Solidity development experience, it is possible to integrate our protocol into a custom contract.
Tokens will be minted by Legitimate and made claimable if Legitimate is deploying the contract as well. As part of our hosted services, we can enable brands and creators to sell or give the end customer the items first without requiring wallets or crypto transactions.
The required permission can also be granted to third party wallets or smart contracts to directly manage the minting process.
Our contract can also be modified and extended for an on-chain mint directly by potential holders as well. In the case of web3 native projects, tokens can be minted by the owner's wallet with some modifications to our contract permissions and the token will automatically enter a locked state.
Required changes include making the
For convenience, here's an example of how to interact with our APIs to verify Legitimate's NFC tags in your own application
The following code snippet is an example of a synchronous, blocking javascript function to verify the digital signatures emitted by Legitimate's NFC tags.
This code is provided as an example for your own implementation. For more information on how to implement this exact code into your own website, please see .
The code of the javascript is expanded below for reference.
https://tap.legitimate.tech/?uid=XXXXXXXXXXXXXX&ctr=YYYYYY&cmac=ZZZZZZZZZZZZZUpon successful contract deployment, Legitimate will assign our Gnosis Safe with this role and revoke all other wallets from the admin role.
The API_DELEGATE_USER role is the only core role that is necessary to operate the Legitimate protocol. This role grants a contract address or wallet address the ability to modify the locked state of individual tokens, as well as call the claim function to transfer tokens that are owned by the API_DELEGATE_USER address to other addresses without toggling the locked state.
In the case of Legitimate's hosted services, Legitimate will use this permission to allow users to claim a token associated with each LGT Tag through the claim() function. We will also use this permission to unlock tokens as well using setTokenLock(uint256 tokenId, false).
When using Legitimate's web3 native services, a separate contract can be granted this permission to perform unlocks according to conditions set on that contract including verifying LGT Tag checksum on-chain.
A third-party customer support wallet can also be given this permission to manually unlock or process token claims if there are issues.
The NFT manager role allows Legitimate to grant third parties such as agencies or creators the ability to change the base_url of the token to update the token metadata and mint tokens without giving away the DEFAULT_ADMIN_role.
This role enables a wallet to set the service status of all tokens associated on the contract and can be used to unlock all tokens permanently when the given product's activation period is over.
In physical retail, brands and creators may want to process returns or reset ownership of the tokens after a secondary resale. This role can be assigned to third party customer service representatives or used by Legitimate's hosted services to process returns and reset the digital experience.
Legitimate can also reset the ownership of the tokens in the case of secondary resales so that the new owners of the physical goods can obtain the tokens as well. Specific mechanics of the reset is configurable depending on the creator or brand's needs.
For web3 native clients and projects, this role may not be necessary and should be disabled prior to contract deployment.


By extending these contracts, you will automatically gain the functionality needed to start leveraging the Legitimate protocol.
If you want to leverage Legitimate's serviced offerings, we recommend extending our serviced extensions of the core contracts.
The LGTServiced721 Contracts add additional business logic to support your connected products in the real world, such as recovery mechanisms and service periods. These contracts also leave the flexibility for you to define additional add-ons like metadata and royalties.
For examples on how to extend these contracts, see our examples.
mint()For more info on how to customize the contract, see Customizing the Locked721 Contracts.
Content-Type
application/json
uid
string (14 hex characters)
The unique ID of the tag
ctr
string (6 hex characters)
The nonce of the scan
cmac
string (20 hex characters)
The digital signature of the tag
tamper?
string (2 chars, CC for closed, OO for opened)
Tamper proof status of the tag (optional, only available with NFC tags with tamper detection capabilities)
{
uid: 'AABBCCDDEEFF00, // 16 hex characters
verified: true,
nft_chain_id: number, // optional
nft_contract_address: string, // optional
nft_token_id: number, // usually corresponds with serial_number
name: string, // optional
description: string, // optional
image_url: string, // optional
animation_url: string, // optional
sku_id: number,
serial_number: number, // auto assigned by order the tag is programmed in the SKU
}{
errors: {
cmac: "has expired" | "is invalid",
tag: ["could not be found"]
}
}Content-Type
application/json
uid
string (14 hex characters)
The unique ID of the tag
ctr
string (6 hex characters)
The nonce of the scan
cmac
string (20 hex characters)
The digital signature of the tag
walletAddress
string (40 hex chars with 0x header)
EVM based wallet address of each unique user
{
hash: string // hash of on-chain transaction, tx may not be confirmed yet
}{
error: "This tag has not been enabled for claiming." |
"This NFT has already been claimed and is no longer held by Legitimate." |
"Session expired. Please tap the Legitimate Tag and try again."
}ctrcmacWhen integrating Legitimate into a native app, you must call our APIs to verify the digital signature payload that is present in the query parameters.
You can implement this verification yourself using our API Resources to create a more robust user-experience.
Legitimate implemented a simple on-chain metadata contract that is useful for tokens of a singular SKU or collection that all leverage similar metadata. This on-chain metadata contract does not provide for a separate set of metadata for the locked state.
This contract can be found here.
Off-chain metadata can also be used. Examples can be found here.
The base_uri can be an IPFS folder or any HTTP/S folder containing files 1, 2, 3, ..., locked files in JSON format without the .json extension. Do not include the trailing / in the URI. The file locked in the folder is used instead of the respective file that corresponds to the tokenId when the token is in the locked state.
On our standard smart contract, the NFT_MANAGER_ROLE is required to update the metadata URI.
Base URI examples:
Metadata filename examples:
https://verify.legitimate.tech/?uid=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX&ctr=YYYYYY&cmac=ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZhttps://ipfs.io/ipfs/<folder-hash>
https://www.example.com/token-metadata1
2
3
lockedWhen the activation period of a set of phygital products is over, the brand or creator can decide to turn off the locking mechanism and permanently unlock all tokens by setting the service status to false. This allows the token to be freely traded separately from the physical product without having to unlock.
Each contract managed by Legitimate contains a service status flag. When the service is active, the locking mechanism of the protocol will work as intended. When service is inactive, two things will happen:
getTokenLock() and locked() will always return false
Tokens will no longer auto-lock after transfer
Whether the service status is active or inactive is set here. This can only be set/changed by SERVICE_STATUS_ROLE
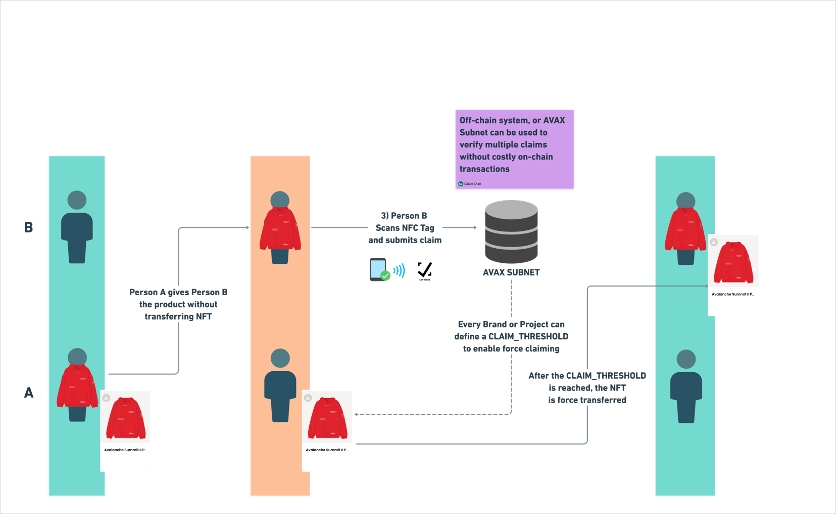
Legitimate can also define token recovery users to help brands reconcile ownership when a phygital product exchanges hands without the underlying token being transferred first. This is done via the TOKEN_RECOVERY_ROLE.
By default, Legitimate operates an off-chain token recovery mechanism that can help brands reset the ownership of their phygital products.
This role can also be granted to a smart contract that operates a decentralized consensus mechanism in conjunction with the ability to verify the NFC digital signatures. As such, this contract can request that the customer scan the unit a set number of times before force recovery is performed.
By leveraging Legitimate's serviced infrastructure, you can take advantage of features such as:
No hassle blockchain deployment and transaction management
Flexible web app front-end ( )
Built in consumer authentication and CRM pipeline.
Collect emails and phone numbers
Robust data and analytics pipeline (fully GDPR-compliant)
Analyze and track where your most loyal customers are
Customizable digital content management (via integration)
Provenance and traceability management
Compliant with most pending DPP proposals
All enterprise deployments leverage Legitimate's service level contracts, found . We introduce a few additional access control roles as well, which can be found .
This is a preview of our protocol. All documentation here is still work in progress.
The Legitimate Protocol is an secure decentralized framework designed to keep physical products in-sync with unique digital identities, specifically from an ownership and provenance perspective. When integrated into the Legitimate Protocol, a product is capable of becoming a phygital (physical + digital) product.
NFC Tags operating on the Legitimate protocol can be by used by customers to verify the authenticity and ownership of physical goods through Legitimate's infrastructure and decentralized smart contracts.
NFC tags powered by the Legitimate protocol have a few key features:
Unique Digital Identity
A decentralized digital ID that satisfies most provenance and traceability protocols, designed to track products through their entire lifecycle. Owners can scan the NFC tag to claim ownership of a product.
Secure
The Locked721Base smart contract is an implementation of ERC-5192.
However, the Locked721Base contract adds additional functionality that makes the tokens locked state mutable.
Each token can be locked or unlocked individually, providing granular control over the locked state.
ILocked721Base provides the high level interface for setting and getting the locked state of each token. Furthermore, ILocked721Base defines claim, which is a function designed for API_DELEGATE users to transfer locked tokens without modifying their locked state.
Locked721Base is the implementation of the interface. This adds additional functions that allow third-party contracts and users with the role of API_DELEGATE to modify the locked state of each token.
Locked721Base itself does not implement IERC721. This is intentional in design. Locked721Base is an abstract class that allows developers to chose their own ERC721 implementation. However, Locked721Base provides two helper methods designed to be called within the hooks an ERC721 implementation
This helper function will return true if a token is locked and the option shouldPreventTransferWhenLocked is true
This helper function will iterate through a set of tokenIds and set the locked state to true.
If the calling method is a mint call (the from address is 0x0) and shouldLockTokensAfterMint is set to false, then this function will not set the locked state to true.
This is a configurable option in the contract that defines whether or not tokens should be auto-locked after mint. By default, this is set to true.
This is a configurable option that determines whether any token in a locked state can be transfered successfully. If this flag is set to true, any transaction that attempts to transfer a locked token will revert. By default, this is set to true.
Legitimate provides two default implementations of Locked721Base: Locked721 (an implementation of OpenZeppelin's ERC721 contract) and Locked721Psi (an implementation of ERC721Psi).
Each of these are representative of their own ERC721 implementation. We won't get into too much detail about each of the underlying ERC721 implementations, but we will cover how both of these contracts implement Locked721Base.
These hooks call _shouldPreventTokenTransfer to determine whether or not locked tokens can be transferred by their owners.
These hooks call _lockTokensAfterTransfer to set the locked state of the transferred tokens after a transfer.
Content-Type
application/json
uid
string (14 hex characters)
The unique ID of the tag
type?
claim | reset | mint
Type of ownership change recorded on the blockchain (optional)
page?
integer
Page number of pagination (optional)
limit?
integer (max 1000)
Number of items in each page (optional)
{
verifications: [
{
created_at: '2023-10-25T09:13:31+00:00',
verify_type: 'programming_qc' | 'user_view' | 'custom',
// only if verify_type === 'custom', otherwise null
custom_verification_type: {
id: 1,
name: "My custom verification defined in Dashboard"
},
uid: "AABBCCDDEEFF00",
tamper: false,
counter: 5,
city: 'Aobadai',
region: 'Tokyo',
country: 'Japan',
latitude: 35.6509,
longitude: 139.6943
}
]
}{
error: {
tag: ["could not be found"]
}
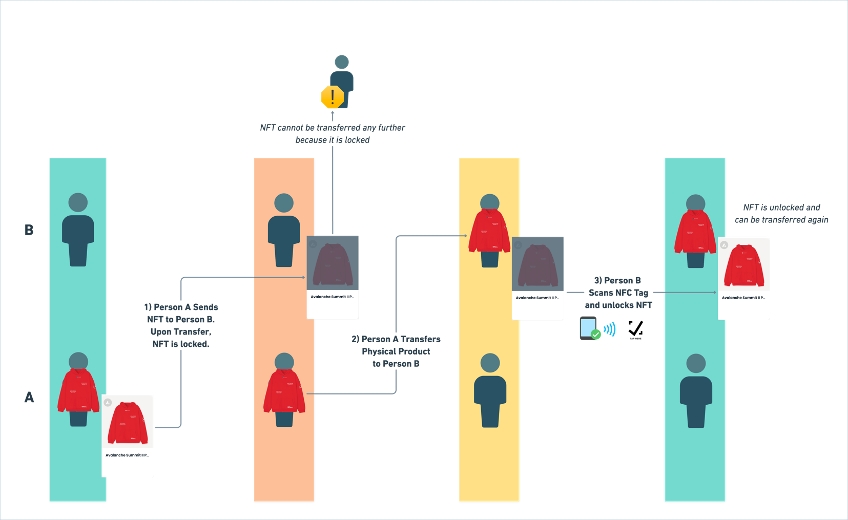
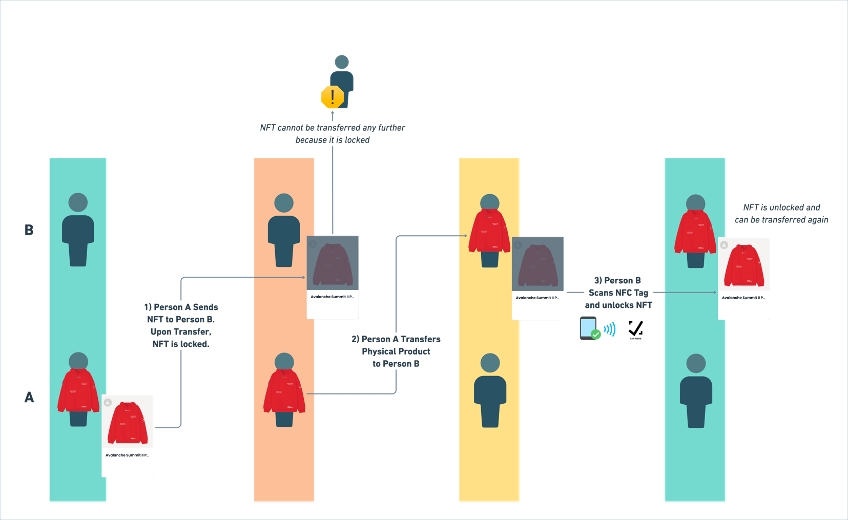
}A digital ID is “locked” and cannot be unlocked or transferred until the NFC tag on the physical product is scanned by the new owner to unlock.
Extensible
Third party developers can build on top of this “locked” digital ID state to provide exclusive gated content, access, and more.
POST /v1/tags/recover
Recovers the digital ID (also known as digital token or NFT) back to the Legitimate wallet to reset the ownership state of the digital ID. The uuid, cmac, and ctr must be from the latest verification. All previous verifications are invalid to prevent users with old links from recovering.
After recovery, the digital ID can be claimed again with the claim API.
Headers
Content-Type
application/json
Body
uid
string (14 hex characters)
The unique ID of the tag
ctr
string (6 hex characters)
The nonce of the scan
cmac
string (20 hex characters)
The digital signature of the tag
Response
{
hash: string // hash of on-chain transaction, tx may not be confirmed yet
}{
error: "Unauthorized" |
"Ownership reset has not been enabled for contract ${contract.address} by ${walletAddress}." |
"Transaction failed with message: ${error.message}"
}
Retrieves a list of ownership transfer records for the specified tag UID.
The type query parameter is required to determine the kind of transfer (mint, claim, or recover).
For mint and claim, the receiver parameter must be provided. sender must not be present.
Requests that provide unexpected or missing parameters will return a 406 error.
Unique ID of the tag
ABC123TAGUIDType of transfer (mint, claim or recover)
Sender wallet address
Receiver wallet address
A list of tag transfers
Tag not found (invalid UID)
Invalid or unexpected parameters
Validates a cmac token for a tag using its UID, counter, and truncated cmac value. Returns tag content and metadata if validation succeeds.
Unique ID of the tag
ABC123TAGUIDCounter used in CMAC generation
00000045Truncated CMAC token from the tag
9f5e6a1ccmac is valid
Tag not found (invalid UID)
Invalid or outdated cmac
Sets the user's email marketing consent status via a GET request. Intended for use with email links where users confirm their subscription choice. Accepts the user's email and a subscribe flag ('true' or 'false'). If one or more user accounts are found with the email, their consent preference is updated.
Indicates whether the user consents to marketing emails
The user's email address
Consent successfully updated
No user found with the given email
Validates a cmac for a tag using its UID, counter, and key. If valid, it checks whether the cmac corresponds to the most recent registered tap of that tag. Returns tag details and the latest verification entry if successful.
Unique ID of the tag
ABC123TAGUIDCounter used in CMAC generation
00000045Truncated CMAC token from the tag
9f5e6a1ccmac is valid and latest
Tag not found (invalid UID)
Invalid or outdated cmac
For recover, the sender parameter must be provided. receiver must not be present.
POST /external/v1/tags/cmac/validate HTTP/1.1
Host:
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: */*
Content-Length: 57
{
"uid": "ABC123TAGUID",
"ctr": "00000045",
"cmac": "9f5e6a1c"
}{
"cmac_verified": true,
"page_content": {
"type": null,
"version": null,
"data": null,
"options": {}
},
"tag": {
"uid": "17261BVD8B1816",
"tamper": null,
"counter": 48,
"created_at": "2025-06-01T13:12:44.000Z",
"updated_at": "2025-06-20T09:42:18.000Z",
"name": "Sport Mixtape Collection",
"description": "The 'Speed Anthem Vol. 1' is a custom launch edition of the SportTrack RS-Z designed by CoreStudios and DJ Elan, with exclusive tracks, remixes, and video clips dropping every week.<br/><br/>Tap your tag to start streaming bonus content. [Read more](https://support.example.com/product-guide/sport-mixtape).",
"image_url": "https://cdn.example.com/images/sport-mixtape-cover.webp",
"animation_url": null,
"notes": null,
"redirect_url": null,
"template_id": 208,
"page_content": {
"type": null,
"data": null,
"version": null,
"options": {}
},
"shareable": false,
"nft_chain_id": 137,
"nft_contract_address": "0xa8cC9F4501B1d0b19A67E36b7e62C999F2345678",
"nft_token_id": 492,
"contract_version": 3,
"verifications": 31,
"external_verifications": 7,
"qc": true,
"tamper_enabled": false,
"login_type": 2,
"header_logo_url": null,
"builder_io_api_key": "e2d89f4017a346edb9beee1234f8d4d9",
"builder_io_url": "/b/e2d89f4017a346edb9beee1234f8d4d9/sport-mixtape",
"tag_view_verifications_count": 29,
"owner_address": null,
"email_marketing_consent": null,
"claim_count": 2,
"reset_count": 1,
"page_type": "builder_io",
"total_tags_count": 492,
"serial_number": 492,
"owner_email": null
}
}GET /external/v1/marketing_consent?subscribe=true&email=name%40gmail.com HTTP/1.1
Host:
Accept: */*
{
"message": {
"email_marketing_consent": "[email protected] subscribed"
}
}POST /external/v1/tags/cmac/latest HTTP/1.1
Host:
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: */*
Content-Length: 57
{
"uid": "ABC123TAGUID",
"ctr": "00000045",
"cmac": "9f5e6a1c"
}{
"cmac_verified": true,
"page_content": {
"type": null,
"version": null,
"data": null,
"options": {}
},
"tag": {
"uid": "04603DCA9C1790",
"tamper": null,
"counter": 32,
"created_at": "2025-05-07T17:25:46.075Z",
"updated_at": "2025-05-23T21:13:17.844Z",
"name": "Puma Mixtape Samples",
"description": "The Evolution of Mixtape Vol. 2 is a special edition of the Puma RS-XL created in 2023 by Alexander-John and Emory Jones in partnership with Roc Nation.<br/><br/>Exclusive content including unreleased tracks, music videos, and more will be added every week after release.<br/><br/>Login to start listening. [Learn more](https://support.legitimate.tech/en/collections/4255487-puma-product-owner-s-manual).",
"image_url": "https://imagedelivery.net/gzjejBRZvh-5ZMasSQlGQA/47769768-7234-444d-5919-2e7128fa0400/public",
"animation_url": null,
"notes": null,
"redirect_url": null,
"template_id": 193,
"page_content": {
"type": null,
"data": null,
"version": null,
"options": {}
},
"shareable": false,
"nft_chain_id": 43114,
"nft_contract_address": "0x5774Fb705c21F0CD29AE1F950bB3AD66D3d82492",
"nft_token_id": 206,
"contract_version": 3,
"verifications": 24,
"external_verifications": 9,
"qc": true,
"tamper_enabled": false,
"login_type": 1,
"header_logo_url": null,
"builder_io_api_key": "a6378b4031b246ebad5efa7540a24082",
"builder_io_url": "/b/a6378b4031b246ebad5efa7540a24082/puma-mixtape",
"tag_view_verifications_count": 23,
"owner_address": null,
"email_marketing_consent": null,
"claim_count": 0,
"reset_count": 0,
"page_type": "builder_io",
"total_tags_count": 206,
"serial_number": 206,
"owner_email": null
},
"verification": {
"id": 5978,
"tag_id": 48941,
"cmac": "6C3BC119371FBFFB",
"created_at": "2025-06-23T22:45:26.327Z",
"updated_at": "2025-06-23T22:45:26.327Z"
}
}{
"transfers": [
{
"id": 108,
"tag_uid": "042C306A2817260",
"nft_token_id": 2,
"sender_address": null,
"receiver_address": "0x803d7be89C5880bEA2F13bc62718a4846f801CFD",
"transfer_type": "transfer",
"created_at": "2011-05-28T20:52:34.154Z",
"sender_email": null,
"receiver_email": "l*****@d********.c**"
},
{
"id": 107,
"tag_uid": "042C306A2817260",
"nft_token_id": 2,
"sender_address": null,
"receiver_address": null,
"transfer_type": "claim",
"created_at": "2024-05-28T19:49:49.574Z",
"sender_email": null,
"receiver_email": null
}
]
}GET /external/v1/transfers/{uid} HTTP/1.1
Host:
Accept: */*
(function() {
// Inject CSS to hide body and error container
const style = document.createElement('style');
style.innerHTML = `
body { display: none !important; }
`;
document.head.appendChild(style);
const API_URL = 'https://api.legitimate.tech/external/v1/tags/verify';
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
console.log('DOM loaded, making API request');
fetch(API_URL, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(new URLSearchParams(window.location.search)))
}).then(async res => {
const data = await res.json();
if (!res.ok) {
if (res.status === 422 && data.errors.cmac.indexOf('has expired') !== -1) {
renderErrorMessage('expired_cmac');
} else {
renderErrorMessage();
}
return;
}
if (!data.errors) {
style.innerHTML = `
body { display: block !important; }
#legitimate-custom-error-message { display: none !important; }
#legitimate-expired-cmac-message { display: none !important; }
`;
} else {
renderErrorMessage();
}
})
.catch(() => {
renderErrorMessage();
});
});
function renderErrorMessage(errorType = 'default') {
let errorContainer = document.getElementById('legitimate-error-message-container');
if (!errorContainer) {
console.log('Creating error message container');
errorContainer = document.createElement('div');
errorContainer.id = 'legitimate-error-message-container';
document.body.appendChild(errorContainer);
}
let errorContent = `
<div style="font-family: sans-serif; color: red; padding: 2rem; text-align: center;">
An error occurred. Please try again later.
</div>
`;
if (errorType === 'expired_cmac') {
const expiredCmacErrorEl = document.getElementById('legitimate-expired-cmac-message');
if (expiredCmacErrorEl) {
console.log('Using expired cmac error message');
errorContent = expiredCmacErrorEl.innerHTML;
}
} else {
const customErrorEl = document.getElementById('legitimate-custom-error-message');
if (customErrorEl) {
console.log('Using custom error message');
errorContent = customErrorEl.innerHTML;
}
}
errorContainer.innerHTML = errorContent;
style.innerHTML = `
body { display: block !important; }
body > *:not(#legitimate-error-message-container) { display: none !important; }
`;
}
})(); <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Script Test</title>
<script src="verify-sdk-v1.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.tailwindcss.com"></script>
</head>
<body class="min-h-screen bg-gray-50">
<main class="container mx-auto px-4 py-8">
<h1 class="text-4xl font-bold text-gray-900 mb-4">Main Page Content</h1>
<p class="text-lg text-gray-600">If the API is valid, you'll see this content.</p>
</main>
<!-- Custom Error Message -->
<div id="legitimate-custom-error-message" class="hidden">
<div class="min-h-screen flex items-center justify-center bg-gray-50">
<div class="max-w-md w-full p-6 bg-white rounded-lg shadow-lg">
<h1 class="text-3xl font-bold text-red-600 mb-4">Custom Error!</h1>
<p class="text-gray-600">This content failed to load. Please contact support.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Expired CMAC Error Message -->
<div id="legitimate-expired-cmac-message" class="hidden">
<div class="min-h-screen flex items-center justify-center bg-gray-50">
<div class="max-w-md w-full p-6 bg-white rounded-lg shadow-lg">
<h1 class="text-3xl font-bold text-red-600 mb-4">Please Scan the Tag Again</h1>
<p class="text-gray-600">The tag verification has expired. Please scan the tag again.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>